You may recall a blog we posted in February that referred to your DPF as a "garbage can" for your diesel exhaust sytem. Today we delve into this concept further, we take a look at common part failures that your diesel particulate filter may be covering up.
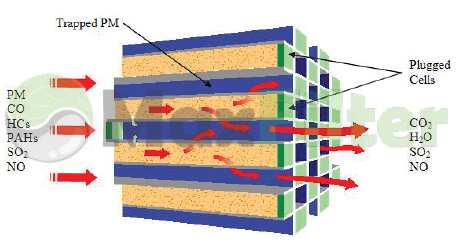
Thanks to the implementation of the DPF in your exhaust system, the days of diagnosing problems by increasing idle RPM's and examining the exhaust are gone. We also know that not all soot can be burned during regeneration, leaving ash in the body of the filter.
As referenced by the California Air Resources Board (CARB), here are 5 ways that parts of liquids could increase soot and plugging in diesel particulate filters if you do not follow a regular maintenance schedule:
- Fuel Injectors: As oil leaks into the fuel through failing fuel injectors, excessive fueling will result ultimately creating an increase in soot generation and accumulation in your filter.
- Air Filters: Dirty air filters reduce ambient air flow to your engine. This restricted air flow will lead to increase soot in the diesel particulate filter.
- Turbochargers: Leaking seals or failing turbochargers that do not produce sufficient air flow will lead to increased soot generation.
- Fuel Filters: A black or darkened fuel filter may be a sign that oil from the crank case is mixing with the fuel. This would result most likely from a leaky injector.
- Coolant: Leaking coolant can harm the DOC which serves as a catalyst to the DPF. This leak can cause the DPF to plug sooner as the regeneration process may be affected. If not diagnosed correctly, the coolant leak could easily be overlooked.
Click here to see how a diesel particulate filter works.
Source: " A Truck Driver's Guide to Care and Maintenance of Diesel Particulate Filters" .www.arb.ca.gov/truckstop




